Way to receive inheritance money from overseas
Here's a quick roundup of the best money transfer services to receive inheritance from abroad.
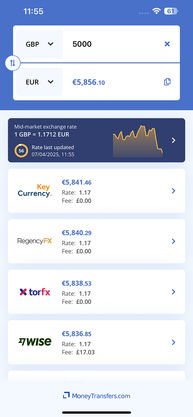
Wise is the best provider for large inheritance transfers. They offer the mid-market rate on currency exchanges, so you'll get exactly what your inheritance is worth when it's exchanged.
Fees are also reasonable, and you can calculate them online or in the app before you send any money as well as see how much the receiver will get.
With a large transfer limit of $1.2 million, you might be able to receive your inheritance in one go, rather than splitting it into different chunks and potentially getting charged for each transfer.
Wise frequently receives positive reviews on Trustpilot, Google Play, and the App Store. Most report a good fee structure and efficiency, along with how easy it is to use the service.
Our video review of Wise
With no maximum transfer limits, OFX is a good way to receive your inheritance from abroad.
They charge no fees on their transfers and add a small markup to their currency exchange rates.
They also service over 170 countries, with more than 50 currencies available.
OFX lets you monitor the exchange rates available before you make your exchange, so you can change the currency of your inheritance when to get a better deal.
The OFX fee structure is more opaque than some other transfer services, with no calculators available for their exchange rates, and customer reviews remain mixed.
Another provider with no limits, KeyCurrency is a good option for receiving your inheritance.
They don't charge fees for their transfers, but they only process bank transfers, and their serviced countries are quite limited.
You'll need to ask the customer service team for a quote rather than calculating fees yourself, and transfers can be slow.
But if you need to send a lot of money at once, they may be the provider for you.
Consider this before receiving an overseas inheritance
When transferring a larger sum of money from abroad - regardless of the reason - one of your main concerns will be finding a provider that can send your money internationally for a fair fee and exchange rate not too far from the mid-market rate.
When looking to transfer your inheritance money back to your home country, here are a few things to factor into your decision:
Transfer fees
Most banks and money transfer services will charge a fee for an international transfer. This could be a fixed fee, or it could be percentage-based depending on how much you are sending.
Banks especially are known for charging high fees for international transfers, both for the sender and for the recipient.
That’s why our overall recommendation is to compare money transfer providers to find the best service for you.
If you are receiving a large inheritance from abroad (perhaps $10,000 or more), you may want to look for a specialist transfer broker who facilitates larger international transfers in particular.
Exchange rate
Maximum sending limits
Banks are known for typically charging higher transfer fees and a larger markup on the exchange rate than most money transfer providers, with margins up to 5% added on to the mid-market rate.
For example, receiving an inheritance of $100,000 from overseas could cost you $5,000 simply on the exchange rate when using a bank.
Comparing providers and finding the most competitive fees and closest exchange rate to the mid-market rate is therefore a prudent strategy to avoid losing more of your money to charges than necessary.
Taxes for receiving an overseas inheritance
An inheritance tax is paid by the person who inherits money, property, or other assets from a person who has died.
The amount that is taxable on an inheritance can vary depending on where you are in the world, so we’ve covered the main tax regulations when receiving an overseas inheritance in the UK, US, Canada, and Australia below.
Inheritance tax laws in the UK

In the UK, whether you need to pay tax on an inheritance from overseas largely depends on whether the individual can be considered domiciled out of the UK.
HMRC will recognize a change of domicile when there is clear evidence that the individual in question moved away and planned to live abroad permanently.
A few examples of this could include:
Working abroad
Owning property in a foreign country
Sending children to an overseas school
You should note, however, that HMRC may still consider the UK to be the individual’s official place of residence for inheritance tax if they lived in the UK for 17 of the previous 20 years, or if they had a permanent residence in the UK at any point in the last three years of their life.
The estate is valued below £325,000
Any inheritance above this threshold is left to a spouse or civil partner
Anything above the threshold is left to a charity
Find more information on the UK and inheritance tax from the GOV.UK website.
Inheritance tax laws in Canada

In Canada, there is no inheritance tax.
Therefore, whether you are receiving an inheritance from a relative who is not a resident of Canada overseas, or from a recognized Canadian citizen, your inheritance is not deemed as taxable income - rather, the estate pays all tax before you receive the inheritance.
With that said, you may be subject to taxation on any future income that may be generated from your overseas inheritance, even if it is not remitted back to Canada.
This is because Canadian residents are subject to tax on worldwide income.
Inheritance tax laws in the US
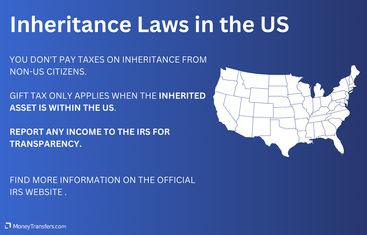
In the US, you will not typically be taxed if you are receiving an inheritance as a US person from a non-US person and the assets inherited are based outside of the US.
The taxes that could come into play when receiving an inheritance from abroad are:
Estate tax - Estate tax does not apply provided the individual bequeathing the inheritance to you was not a US national or a foreign national residing in the US. If the estate is located abroad, the estate tax will not apply. Rather, taxes are the responsibility of the foreign country in which the inheritance/estate is located.
Gift tax - Gift tax is only applicable when the inheritance asset transferred is within the United States. However, multiple rules apply under different circumstances (for example different rules apply for married couples).
However, even if your overseas inheritance is not taxable, you will likely still need to report it to remain transparent about your accounts.
You will need to declare what you have been paid on your US tax return using Form 706-CE, which is Certification of Payment of Foreign Death Tax.
Completing this form will ensure the IRA knows that tax was paid on the inheritance you received before it was transferred to you.
Find more information on US estate and gift taxes from the IRS website.
Inheritance tax laws in Australia
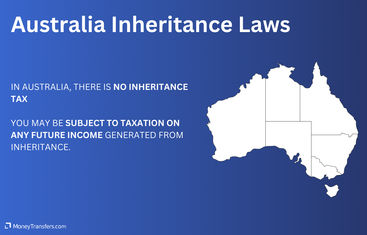
An overseas inheritance is not taxable in Australia.
The only time there might be tax implications in Australia is if a part of the inheritance could continue to earn an income after the individual’s death.
For example, earning interest on a savings account or dividends from stocks If this applies to you, a tax return would be due on any income that is taxable from the estate until it has been administered in full.
Find out more about inheritance and tax obligations on the Australian government website.
A bit more on receiving inheritance from abroad
Do money transfer services offer advice on inheritance tax?
Why not use a bank to receive inheritance?
Help & FAQ
Get answers to the most common questions asked when sending money abroad. Covers costs, fees and the best way to compare.
Let's recap: Know the law to avoid being caught out
Even if inheritance tax does not apply in the country you are residing in, it’s important to make sure you are aware of any legal obligations or responsibilities you need to uphold when receiving an inheritance from abroad.
Equally, you’ll want to make sure you are using a suitable transfer broker when receiving your inheritance into your bank account.
Verifying that the company in question can transfer the funds without hitting the maximum sending cap and that you are not losing vast amounts of money in fees are two essential considerations.



.svg)