How to Send Money Without CVV in 2026
You can make payments safely without a CVV by arranging bank transfers, using a P2P payment app, or even sending cash.
Your CVV is an important layer of security used when making online purchases or payments by card.
It helps verify you and confirm you're using your card, helping to prevent credit card fraud. However, you can make payments online without one.
Read on for more details on safely sending money without a CVV.
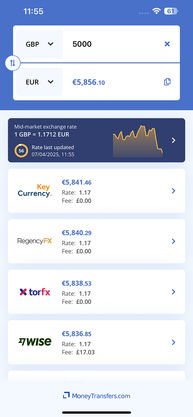
Search Now & Save On Your Transfer
CVV explained
A CVV (Card Verification Value) is a security code on the back of your debit or credit card that helps protect you from fraud.
It’s used to prove you have the debit or credit card you’re using and helps protect your account if your card number should fall into the wrong hands.
Your CVV is also known by other names, including:
Card Security Code (CSC)
Card Verification Code (CVC)
Card Validation Code 2 (CVC2)
Card Identification Number (CID)
What’s the difference between CVC1 and CVC2?
The CVC1 is the card validation code encoded on the card's magnetic stripe. This code is not visible and is unique to your card. The CVC2 is the same as the CVV; it’s the three-digit number printed on your card's back.
Where to find your CVV
Your CVV is printed on the back of your card.
It’s usually a three-digit number, but with American Express, it’s a four-digit number.

Each CVV is unique to the card and account holder and will change if you get a new card.
Your CVV is not your PIN
It’s important to note that a CVV is not your Personal Identification Number (PIN). You should never provide your PIN when paying for something online.
Sending money without CVV number
If you want to make an online payment with your card, you'll usually need your CVV to process the payment.
However, if you’re using a money transfer service, there may be some equally secure alternatives that you can use instead. These include:


Using a P2P payment service
If you're making a purchase online, you could use peer-to-peer payment apps like PayPal.
To do this, you'll need to have a card or bank account linked to your PayPal account.
When you're first linking your card details to your PayPal account, you will need to provide:
Your CVV
Your 16-digit card number
The expiration date
Alternatively, you can link your bank account to your PayPal account, which will require your bank account number and branch/sort code.
Once you’ve linked these details, you won’t need to provide your CVV number for online transactions when using PayPal; these details will already be stored.
Many online retailers offer PayPal as a payment option, meaning you simply need your email and password to verify the purchase.
Just log in to your PayPal account and you won't need to enter your card details again into the retailer’s website.
Using a digital wallets
Sending money by bank transfer
Sending money as cash
Wise is a good option for sending money without CVV. You can either top up your balance via Apple Pay or Google Pay, or use your bank.
Both options don't require a CVV number.
Once your balance is topped up, you can use it to send money abroad or domestically.
"Over 16 million customers use Wise, mostly for their excellent mobile app, transparent fee structure & use of mid-market rates. Now increasingly used for larger transfers."
"Over 16 million customers use Wise, mostly for their excellent mobile app, transparent fee structure & use of mid-market rates. Now increasingly used for larger transfers."
"Over 16 million customers use Wise, mostly for their excellent mobile app, transparent fee structure & use of mid-market rates. Now increasingly used for larger transfers."
How a CVV protects your account
A CVV is an extra layer of security that increases the likelihood that it’s you making the payment.
Requesting a CVV makes it harder for fraudsters to authorize payments with your card details if they don’t have the physical card with them.
Key benefits of using a CVV code when sending money
There are some key benefits to using a CVV code when making an online purchase. These include:
Protection against fraud
If someone gains access to your card details, they won’t be able to make a payment without your CVV.
Merchant’s can’t reuse CVVs
When you’ve purchased with a merchant, they may allow you to store your card details with them online.
Merchants are not allowed to store your CVV.
This helps stop you from overspending accidentally and prevents merchants from using your card without your authorization.
Services and stores that don’t need a CVV
As it’s only an optional additional security measure, not all need you to provide a CVV to buy something.
Some well-known names that don’t need a CVV include:

Amazon
Your card information is stored directly on Amazon account. You won't need to enter the CVV unless you're adding another payment method.

Walmart
Similarly, Walmart will store your bank details and let you re-use them on the next purchase.

Target
Target will store the CVV with no access to it. This will let you check out faster and won't require any details.

Apple Pay
You add your card to the Apple Pay along with your CVV. This information is stored for faster checkout at any store accepting it.

Google Wallet
Similarly, Google Wallet is connected to your bank account along with your CVV. The information is encrypted and allows you to pay directly from your card without needing the CVV code.

PayPal
When setting up PayPal, you enter your bank card details into the account. These are saved for future transactions.
When you're ready to pay, all you need is your PayPal account details and that's it.
Stores like these allow you to transfer money over using only your card number, and not your CVV.
Why some stores don't need a CVV for card payments
Most stores that don’t need you to provide a CVV when you make a card payment have other layers of security in place. These may include:
Address Verification System (AVS)
This cross-references your address and compares it to the address on file for the card.
Bank confirmation
The store may send you to your banking app so you can verify your payment remotely.
External payment apps
External payment apps like PayPal, Google Pay, and Apple Pay have your card details stored on file.
To verify your payment, you just need to log in to your account; you don’t need to enter your CVV again.
You may also find that some larger retailers simply have a higher risk tolerance than others.
They could potentially be prepared to absorb the costs of potential fraud and chargebacks, but this does not make it safer for you.
If you’re paying by card, entering your CVV helps protect you from potential fraudsters.
Be careful where you input your details
Make sure the store page you’re on is legitimate and respectable before entering your card details. Scammers sometimes create fake shopping sites to capture your payment details.
Find out more about online shopping scams, phishing scams, and other common money transfer scams on our scams page.
A bit more on CVVs
How do thieves use stolen debit cards?
Do credit card thieves get caught?
Is it safe to give PayPal my CVV?
Can someone use my debit or credit card without the CVV?
How can I transfer money from my credit card without a CVV code?
Help & FAQ
Get answers to the most common questions asked when sending money abroad. Covers costs, fees and the best way to compare.
Let's recap: CVVs - an extra layer of protection for your card payments
CVVs are an important layer of security. They help verify your identity when making payments online, adding another layer of protection should your card details fall into the wrong hands.
This is why your CVV is often an essential requirement when making an online payment and sending money.
For international money transfers, the best way to avoid using your CVV is to send money via a bank transfer with a money transfer provider (this means you won’t need to provide your card details).
Get started by finding a money transfer provider that suits your needs using the form below.
Send money without providing your bank details
Sources & further reading
Related Content


Contributors