What is the Mid-Market Exchange Rate?
If you've ever exchanged money, you've probably noticed the difference in the exchange rates between banks.
However, have you ever wondered who sets these rates? And why the exchange rate can vary so wildly between banks and other providers?
Here, we’re looking at exactly what is mid-market rate and why it’s so important to be aware of when sending money abroad.
Search Now & Save On Your Transfer
Mid-market rate explained
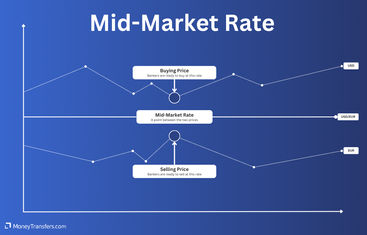
The mid-market rate, also known as the middle or interbank rate or spot rate, is the midpoint at which banks trade currencies with one another.
In other words, the mid-market exchange rate is the middle point between the price for buying and selling currencies at any given time and is therefore naturally set by the market as it fluctuates.
How is the exchange rate set?
The exchange rate impacts the cost of one currency about another, but who sets these exchange rates? Who decides how much a US Dollar should be worth in comparison to the Pound Sterling?
This rate is usually set by banks, financial providers, and other financial institutions. Each of them sets their rates (usually once a day) and that's why it always varies from bank to provider.
Some financial institutions such as ECB keep track of these rates on average and provide them for informational purposes.
However, there is a baseline to this, the 'real' exchange rate, and it's called the mid-market rate.
Then, who sets the mid-market rate...?
The mid-market rate is set naturally in the market. This is because (as previously mentioned), it is the midpoint between the buying and selling prices of two currencies on the open market that bankers use.
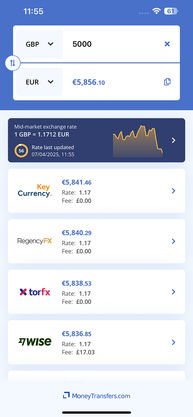
What is the mid-market exchange rate today?
Here's the current mid-market exchange rate for EUR to USD (use the drop-downs to change the currency pair).
What affects the mid-market rate?
Global forces, demand and supply, and economic influences will also influence the exchange rate between any given currency pair on an ongoing basis, which is why the mid-market exchange rate is susceptible to change constantly.

Supply and demand
The value of a currency is influenced by how much of it is available (supply) and how much people want it (demand). High demand for a currency, often due to investment or trade, increases its value, while high supply, such as through central bank actions, can decrease its value.
Economic indicators
Economic metrics like inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic growth impact currency values. Higher interest rates attract investors and can strengthen a currency, while high inflation typically weakens it by reducing purchasing power.

Politics
Political events, including elections and policy changes, as well as the general stability of a government, affect investor confidence. Stable political environments usually support a stronger currency, whereas political turmoil can lead to depreciation.
Market speculations
The actions and expectations of traders in the Forex market can drive currency values up or down. Speculation based on predicted economic events or market movements plays a significant role in setting the mid-market rate.

Global trade
A country's trade balance impacts its currency value. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) usually strengthens a currency, while a trade deficit can weaken it. Commodity prices also affect the currencies of major exporting countries.

Capital flows
The movement of capital, such as foreign direct investment and portfolio investment, impacts currency demand. Large inflows of investment increase demand for a country’s currency, boosting its value, while significant outflows can have the opposite effect.

Central bank actions
Central banks influence exchange rates through monetary policy tools like adjusting interest rates and engaging in open market operations. They might also directly intervene in the Forex market by buying or selling their currency to stabilize its value.
For example, in the US, The Federal Reserve (Fed) can significantly affect the exchange rate through various monetary policies. These are usually set a few years in advance, here's a quick summary of the latest projections from the Fed.
In June 2024, the Fed maintained interest rates unchanged, awaiting clearer signs of sustainable inflation progress, with projections signaling a cautious approach to rate cuts and modest adjustments to economic growth and inflation forecasts.United States Fed Funds Interest RateFederal Reserve
Why does the mid-market rate matter to you?
The mid-market rate by itself, will impact how much money you will receive. The better the rate, the more money you will get.
Practical example
Let’s say the current exchange rate is 1 USD = 0.90 EUR. If you have 100 USD, you can send it and the receiver will get 90 EUR (if we exclude all the other fees). If the exchange rate changes to 1 USD = 0.85 EUR, your 100 USD would now be worth 85 EUR.
This rate should be the basis you use to compare the services offered by other money transfer providers and banks to determine whether you are getting a fair deal.
However, many banks and money transfer providers will add a 'markup' to the 'real' rate to make a profit from the transfers (in addition to any other fees).
Sending money at the mid-market rate
Generally, making an international transfer at the exact mid-market rate is impossible, as providers and banks will typically add a small percentage onto the current mid-market price as a fee for sending your money.
Some money transfer providers will be extremely close to the 'real' rate but will add additional fees to the transfer. Whereas other providers might offer more services but add a bit more markup to the mid-market rate and fees on top.

Our analysis
In terms of exchange rates, Wise is your best bet for sending currencies. Based on our 3-month analysis of money transfers from the US to Spain, Wise appeared 100% of the time in our comparisons as the best money transfer provider with the 'realest' rate.
It's worth noting, that although Wise offers the best exchange rate, it doesn't always make them the cheapest because there are other fees involved. Use our comparison tool to get the best deal on your transfer.
The exchange rate you are offered by banks and some providers could be anywhere from 0.1 up to 10% on top of the mid-market exchange rate, which can greatly affect how much money your recipient receives at the other end.
For example, a study on foreign exchange transaction fees has found that the exchange rate margin fees on remittance outflows have increased by 62.61% between 2013 and 2019.
For this reason, researching your options is vital to make sure you find the best service for you, getting the maximum amount to your recipient rather than losing hundreds or even thousands in unfair exchange rates.
Research your options
'Traps' to avoid when converting and sending money
In the modern world, the expectations for fees are high. We expect the fees to go down and the speed to go up. This leaves payment services and banks to get creative with their fee structures to maintain profits.
Here's a list of key 'traps' and pitfalls to avoid when looking for the best exchange rate:
Pricing and fees - You'll often find that banks and other payment services will advertise '0% fees', 'no commission', or 'exclusive rates'. This usually implies that there is a hidden transfer fee or a markup on the mid-market rate.
Competitive exchange rate - These are often showcased to make you believe that it's the best rate on the market and close to the mid-market rate. However, once you start looking, it's very hard to find the exact rate before initiating the transfer.
Receive amount - Not knowing the amount your recipient will get likely means you are being overcharged when sending money.
Avoid banks and providers that are not transparent with their currency conversion fees. Use our comparison form above to find the best rate for your currency transfer.
Getting the most for your money
Understanding what the mid-market exchange rate is will help you get more for your money when you make an international money transfer, but there are other things to think about as well. This includes:
Receiving fees
Some banks will charge a fee to receive money from another country, even if it is being sent in the bank’s native currency. It’s therefore important to not only consider the exchange rate and transfer fees you are being charged but also any charges that may also be applied on the other end.
These fees can all affect how much your recipient ends up with, so is necessary to take into consideration if you are looking to send someone a certain figure.
Lock-in exchange rates
Forward contracts
Help & FAQ
Get answers to the most common questions asked when sending money abroad. Covers costs, fees and the best way to compare.
Let's recap: What is the mid-market rate?
Mid-market rate is a point between the buy and the sell price of a given currency pair. The buy and sell prices are set by the banks and other financial providers based on multiple factors. The mid-market rate settles naturally between them.
The platforms that can move money internationally are making efforts to modernize and innovate their services all the time, so it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with some of the better platforms in the industry.
As increasing competition enters the marketplace, the best option you have for making international transfers could shift from one platform to another.
Use our comparion form to find the best currency deals
References & further reading
Related Content


Contributors

April Summers