What is a bank code?
In this guide we will outline the meaning of a bank code, what they are used for and the various types of codes that are used by banks and other financial institutions around the world.
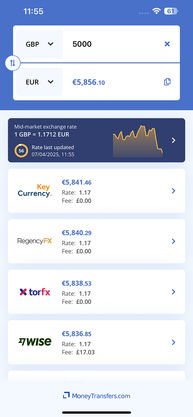
Search Now & Save On Your Transfer
What is a Bank Code?
A bank code is an umbrella term used to describe alphanumeric codes that identify financial institutions. Sometimes bank codes are used domestically to reference banks located within the same country, while other bank codes are used to ID financial institutions abroad.
The rules that distinguish different types of bank codes will be determined by the central bank or governing body which has issued the code. This means the format, length and appearance of a bank code will differ from country to country, and no two bank codes will ever be the same.
SWIFT Codes
SWIFT codes are used by the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication network to identify a bank’s location, country, and branch number when processing an international money order. A SWIFT code will be 8 to 11 characters long and can be located on bank statements, in your online banking or by contacting your bank directly.
BIC Codes
BIC code is a term interchangeable with SWIFT code as they both describe exactly the same thing. Like SWIFT codes, BIC codes are required when transferring funds internationally to an overseas bank account. This type of code is used by financial service providers, as a way of identifying exactly where your money needs to be sent to.
Clearing codes
A clearing code - clearing number or National Clearing Code (NCC) - is called for when you are sending money to a bank account that does not have an International Bank Account Number (IBAN). Typically, a clearing code will not be needed if you have SWIFT/BIC code or an IBAN and are generally used for payments outside of the European Economic Area (EEA).
IBAN
An IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number and this is a code made up of no more than 34 letters and numbers. IBANs are used as a unique identifier for bank accounts when sending and receiving international payments. IBANs are used by banks all around the world to pinpoint the country, bank, and bank account that funds should be deposited to when moving money across borders.
Sort Codes
Sort codes are used by British and Irish banks to identify the location of a domestic bank, so that financial institutions can recognise where the payment has originated from or validate where it is being sent to. Also known as sorting codes, or a national sort code (NSC) in Ireland, these codes can be found integrated into an IBAN (International Bank Account Number) but they have no relation to SWIFT or BIC codes.
Routing numbers
Routing numbers are also known as ABA numbers. It is a 9 digit code used in the USA to identify the location of different financial institutions, in the same way sort codes are used in the UK.
BSB numbers
BSB numbers, also known as Bank State Branch numbers, are used in Australia to identify individual branches of banks and other financial institutions. They function in the same way as sort codes and routing numbers.
IFSC numbers
An IFSC or Indian Financial System Code, is a code used in India to identify different bank branches within the country’s National Electronic Funds Transfer network. This is a system authorized and maintained by the Reserve Bank of India.
BLZ numbers
BLZ numbers, or Bankleitzahl, are the German equivalent of sort codes, routing numbers and BSB numbers, used to identify different bank branches within the country.
Related Bank Transfer Guides
Related Content
Contributors