How do Changes in Currency Exchange Rates Affect International Business?
Currency exchange rates, and understanding how they impact international transactions, are key to successful risk management. Forward contracts, limit orders and multi-currency business accounts all form part of effective risk strategy and mitigating (or benefitting from) the impact of currency fluctuations.
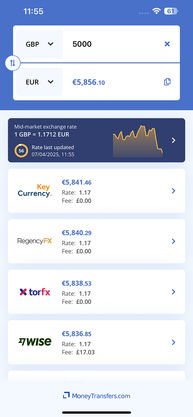
Currency exchange rates can be a confusing subject. Put simply, the better the exchange rate is in your favour, the less it costs to send business payments.
What is a currency exchange rate
Generally, this can be defined as a currency’s value compared to another. This is the rate at which the currency is converted and the number constantly fluctuates based on various factors.
However, the exchange rate can be different at the same time based on what platform you are using to convert the currencies.
The exchange rate paid on business payments is made up of two areas:
Mid-Market Rate
The mid-market rate, also known as the middle or interbank rate or spot rate, is the midpoint at which banks trade currencies with one another.
This rate will change and the worse the rate is, the less received at the other end.
Markup
This is the amount charged on top of the mid-market rate, usually listed as a percentage.
A higher markup can impact the overall amount received.
Impact of each of the different costs
Mid-market rate impact
The mid-market rate changing can have an impact on the total cost of exchanging currency:

Table of data highlighting the impact of a mid-market rate
Getting a worse mark up impact
Some services charge a markup percentage that adds a cost to the end exchange rate. You can compare the rate you are getting against the mid-market rate to figure out what quality of the deal.
Providers offering different mark ups will result in differences in the overall amount received.

Table of data highlighting the impact of a mark up
Sending money as part of a wider risk management plan should be done with both numbers in mind. Fee free transfers aren't always cheaper overall. Better exchange rates will not necessarily mean risk management is included.
We always recommend searching for the typical value of your business transfers to get a clear idea on who the best suited provider is.
Factors impact mid-market and currency exchange changes
It is difficult to predict how the mid-market rate, and subsequent exchange rates, will change over time. However, there are specialist factors that influence the currency exchange rates. Understanding these might clue you in on what macro conditions can lead to the currency rate changing in a specific direction.
Inflation
The rate at which the cost of goods and services rises is inflation. It is expressed as a percentage and can determine how the strength of a currency changes over time.
For instance, if the inflation is lower in the United States compared to other countries, then the US dollar will have more value compared to other currencies.
Interest Rates
When interest rates are increased, then it means that bank account holders will receive a bigger increase in their savings over time.
Therefore, when an economy’s interest rate rises, then investing in that economy is seen as more desirable. Consequently, the demand for the currency goes up and its value. This means the currency's value will rise compared to others, and the exchange rate will reflect this.
Speculation
Speculators can affect the price of a currency by providing an overall consensus that it will go up or down.
The consensus might be based on political events or other market conditions determining whether the economy's strength will increase or decrease.
Currency deficit
When the value of the imports is more significant than the exports, it means that more money is being spent on goods in the country’s currency than is being used to sell. This can create a deficit that leads to the depreciation of the currency.
Public debt
Countries with large amounts of public debt can be risky for foreign investors. Nations may decide to print money to pay for the debt, but that will depreciate the currency's value.
The five factors above are just the tip of the iceberg regarding how the mid-market rate can change between 2 currencies. Businesses need to get a great deal on currency exchange rates to keep costs low for international money transfers. Therefore, keeping an eye on how a currency pair rate changes over time provides insight into what is a great deal.
Exchange rate impact on business
Now let us turn our attention to how currency exchange rates can impact your business. This section highlights the top reasons why you need to pay attention to the currency pairs that your business consistently uses for conversions.
Open-market exchange rate
This can be thought of as the mid-market rate, which is the current official rate. It is usually the best rate that you can get based on current market conditions. Rates charged by banks and money transfer companies typically add a markup percentage to this rate in the pursuit of profiting from the transaction. You should always be aware of the mid-market rate so you can compare the quality of the deal that you are getting.
Foreign currency conversion fees
Most services that offer currency conversions will add a fee. This can be in the range of 1-3% for competitive services, but some banks might charge up to 5% for some currency pairs. This adds a high cost to sending money internationally. On the other hand, business-orientated transfer services like Currencies Direct and TorFX charge competitive markup percentages that will save you money compared to banks.
Supplier payments
Depending on where the supplier is located, you may need to pay for goods in a foreign currency. Ideally, you should find a money transfer company that offers the mid-market rate for these transactions to avoid extra costs. However, your regularly used currency might depreciate or appreciate compared to the supplier’s currency. This should be factored into the cost of the supplies.
Sales forecasts
When selling goods in multiple currencies, it can affect the overall income. Therefore, when a currency in a specific region changes, then you need to factor that into the sales forecast. It can also affect the bottom line, and it could be the case that profitability disappears when the currency conversion rate passes a specific threshold.
Balance sheet hedging
This is a process that allows you to weather unforeseen FX rate changes by holding various currencies. Businesses can balance their risk by spreading their assets among multiple currencies. Therefore, when one currency depreciates compared to another, it will have a minor effect on the business. There are programs that allow for automated balance sheet hedging, which is a great tool to invest in for businesses.
The broader economy
Currency exchange rates can determine the buying force of a market. For instance, if a currency depreciates in a specific country, then their buying power decreases, and residents from that nation are less likely to buy from you. This can help you figure out a fair pricing structure for different regions because you want to price your goods and services at a price that reflects the buying power of that region.
Currency impact on the economy
Overall, a weaker currency means that imports are more expensive. This can reduce the demand for imported goods since their prices will increase. However, when a foreign currency’s value diminishes, the cost of imports decreases, which can increase the demand for those goods.
Additionally, the strength of a currency can contribute to the nation’s trade surplus and trade deficit over time. Generally speaking, businesses want the strength of their commonly used currency to appreciate in value. However, it can be a double-edged sword, because if they have many customers in a nation where the currency is depreciating, there will be less demand for their products in those regions.
Avoid exchange rate fluctuations
In this section, we will look at a few ways businesses can reduce the risks associated with FX rate fluctuations.
Spot contracts: a spot contract money transfer allows businesses to control the currency exchange rate they pay. These payment types pause the transfer until the desired FX rate is matched based on market conditions. This might take a few hours or days to process, but money will be saved until the FX rate improves. Businesses can save money since they do not have to send money if the current currency exchange rates are bad.
Forward contracts: these payment types are settled at a date in the future. This provides businesses with cash flow flexibility. For example, if a business knows they will receive a big payment at the end of the month from goods sold, they can schedule a forward contract to pay suppliers on the same date.
Broker: businesses can hire the services of a broker if they wish to get the best FX rates on the market. A broker's job is to analyze market conditions and provide suggestions on what currency rates businesses should be paying.
Help & FAQ
Get answers to the most common questions asked when sending money abroad. Covers costs, fees and the best way to compare.
Sources and Further Reading
Related Content
Contributors